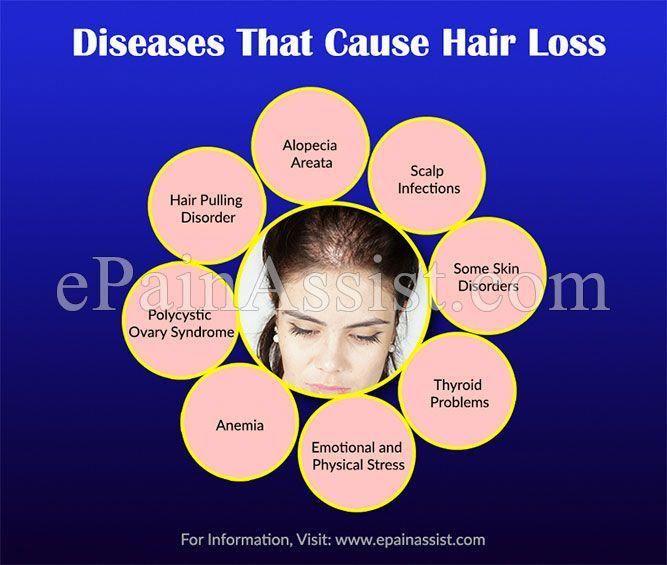
Losing your cat’s fur can be frustrating and upsetting, but it could also be indicative of an underlying issue.
Your veterinarian can diagnose the source of your cat’s hair loss and recommend treatment options. It is essential that they consume a nutritious diet with high-quality nutrients in order to maintain their coat and skin health.
Fleas
Fleas are not only an irritating pest, but they can spread diseases to your pet and you. They have the potential to transmit infections such as bubonic plague and various skin conditions like cat scratch fever and murine typhus.
The flea life cycle begins when a female lays her eggs on an animal of warmth (dog, cat or other). These eggs will hatch into larvae after 24 days in summer and up to 200 in winter. Larvae then transform into pupae which survive in their cocoon for 5-14 days depending on weather conditions before emerging as adults.
Allergies
Allergies are reactions of our immune system to harmless substances in our environment (allergens). Examples include pollen, dust mites, animal dander, mould and certain medications.
Allergy symptoms can range in intensity from mild to severe. The most severe case is anaphylaxis, which could prove life-threatening and requires prompt administration of adrenaline (epinephrine).
People with allergies develop antibodies to an antigen known as immunoglobulin E (IgE). These molecules attach themselves to mast cells in the nose, throat, digestive tract and skin.
Cells then release histamine, which causes redness and swelling. This may also result in itching, hives, or asthma symptoms.

An allergic response can be initiated by a single allergen or it may develop over time when you are exposed to repeated small doses of the same allergen. This condition is known as delayed hypersensitivity and skin tests are used to diagnose it.
Hormones
Hair loss in pets can occur for various reasons, so pet parents need to determine what’s causing the issue and then begin looking for solutions. Once you identify what’s causing the issue, there will be no excuses!
Allergies are a common factor in the development of feline alopecia. These can be both food-related and environmental (e.g., pollens or dust mites).
Parasites can also cause itching and irritated skin in cats. Cats who become allergic to fleas or ticks may develop itching and scaling on their coat.
Hypothyroidism and Cushing’s disease, in which an excess of cortisol is produced, may both contribute to hair loss.
Unfortunately, most causes of alopecia can be addressed with timely evaluation and treatment. It’s important to remember that some cases may be due to underlying diseases that may not respond to standard treatments; this condition is known as feline acquired symmetric alopecia or feline endocrine alopecia. Diagnosing this condition may prove challenging, but your veterinarian is the best resource for assistance.
Stress
Loss of your cat’s fur can occur for various reasons; while bald patches usually indicate illness or an underlying medical issue, it could also simply be part of normal aging processes.
If you observe your cat having an unusually large amount of hair loss, it’s time to bring them in for a consultation at the vet. They can accurately diagnose what’s causing it and offer treatment accordingly.
Cat hair loss is often due to fleas, mites, ringworm, infections or allergies. To check for these issues, use a fine-toothed comb on your cat’s coat at least once every week.
Another potential cause of excessive grooming may be a stressful situation, such as moving to a new home or being bullied by another pet in the household. This behavior, known as displacement grooming, often takes place to relax cats and deflect aggression while reducing their stress levels.

